Knowledge
Collection of Useful Commands
Project maintained by MatthewLaFalce Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
 Collection of Developer Essentials
Collection of Developer Essentials
Created by Matthew LaFalce
 Table of Contents
Table of Contents
![]() Helpful Commands
Helpful Commands
![]() Developer Tools
Developer Tools
![]() Charts
Charts
 Helpful Commands
Helpful Commands
Bundler
# Install a specific version of bundler
gem install bundler -v '1.16.0'
# run a specific version of bundler
bundle _1.16.0_ install
# uninstall bundler
gem uninstall bundler
# uninstall all gems
gem list | cut -d" " -f1 | xargs gem uninstall -aIxCron
# ┌───────────── minute (0 - 59)
# │ ┌───────────── hour (0 - 23)
# │ │ ┌───────────── day of the month (1 - 31)
# │ │ │ ┌───────────── month (1 - 12)
# │ │ │ │ ┌───────────── day of the week (0 - 6) (Sunday to Saturday;
# │ │ │ │ │ 7 is also Sunday on some systems)
# │ │ │ │ │
# │ │ │ │ │
# * * * * * command to execute
# example entries
# every 15 min
*/15 * * * * /home/user/command.sh
# every midnight
0 0 * * * /home/user/command.sh
# every Saturday at 8:05 AM
5 8 * * 6 /home/user/command.shEclipse
ctrl + { #toggle vertical split
ctrl + L #go to line
ctrl + shft + F #auto format
ctrl + shft + / #toggle comment on highlighted sectionFinding Documentation
- Know how to read official documentation with
man(for the inquisitive,man manlists the section numbers, e.g. 1 is "regular" commands, 5 is files/conventions, and 8 are for administration). Find man pages withapropos. - Know that some commands are not executables, but Bash builtins, and that you can get help on them with
helpandhelp -d. You can find out whether a command is an executable, shell builtin or an alias by usingtype command. -
curl cheat.sh/commandwill give a brief "cheat sheet" with common examples of how to use a shell command.
Grep
#-n Show relative line number in the file
#'yourString*' String for search, followed by a wildcard character
#-r Recursively search subdirectories listed
#. Directory for search (current directory)
grep -nr 'your_string' .
# Search a file for a pattern
grep pattern file
# Only Return the matching string
grep -oh pattern file
# Case insensitive search (with line numbers)
grep -in pattern file
# Recursively grep for string <pattern> in folder:
grep -R pattern folder
# Read search patterns from a file (one per line)
grep -f pattern_file file
# Find lines NOT containing pattern
grep -v pattern file
# You can grep with regular expressions
grep "^00" file #Match lines starting with 00
grep -E "[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}" file #Find IP add
# Find all files which match {pattern} in {directory}
# This will show: "file:line my research"
grep -rnw 'directory' -e "pattern"
# Exclude grep from your grepped output of ps.
# Add [] to the first letter. Ex: sshd -> [s]shd
ps aux | grep '[h]ttpd'
# Colour in red {bash} and keep all other lines
ps aux | grep -E --color 'bash|$'Git/Github
lg = "log --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset' --abbrev-commit --date=relative"
up = "!git remote update -p; git merge --ff-only @{u}"
tree = "!git lg --graph"
unstage = "reset HEAD"
last = "log -1 HEAD"
visual = "!gitk"
st = "status"
uncommit = "reset --soft HEAD^"
progress = "diff --stat"
pg = "diff --shortstat"pushFunc(){
git push || git push --set-upstream origin $(git branch | grep \* | cut -d ' ' -f2)
}
alias gp='pushFunc'
alias gs='git status -sb'
alias gc='git commit'
alias gb='git branch'
alias ga='git add'
alias gd='git diff'
alias gt='git tree'# To set your identity:
git config --global user.name "John Doe"
git config --global user.email johndoe@example.com
# To set your editor:
git config --global core.editor emacs
# To enable color:
git config --global color.ui true
# To stage all changes for commit:
git add --all
# To stash changes locally, this will keep the changes in a separate changelist
# called stash and the working directory is cleaned. You can apply changes
# from the stash anytime
git stash
# To stash changes with a message
git stash save "message"
# To list all the stashed changes
git stash list
# To apply the most recent change and remove the stash from the stash list
git stash pop
# To apply any stash from the list of stashes. This does not remove the stash
# from the stash list
git stash apply stash@{6}
# To commit staged changes
git commit -m "Your commit message"
# To edit previous commit message
git commit --amend
# Git commit in the past
git commit --date="`date --date='2 day ago'`"
git commit --date="Jun 13 18:30:25 IST 2015"
# more recent versions of Git also support --date="2 days ago" directly
# To change the date of an existing commit
git filter-branch --env-filter \
'if [ $GIT_COMMIT = 119f9ecf58069b265ab22f1f97d2b648faf932e0 ]
then
export GIT_AUTHOR_DATE="Fri Jan 2 21:38:53 2009 -0800"
export GIT_COMMITTER_DATE="Sat May 19 01:01:01 2007 -0700"
fi'
# To removed staged and working directory changes
git reset --hard
# To go 2 commits back
git reset --hard HEAD~2
# To remove untracked files
git clean -f -d
# To remove untracked and ignored files
git clean -f -d -x
# To push to the tracked master branch:
git push origin master
# To push to a specified repository:
git push git@github.com:username/project.git
# To delete the branch "branch_name"
git branch -D branch_name
# To make an existing branch track a remote branch
git branch -u upstream/foo
# To list all local and remote branches
git branch -a
# To see who committed which line in a file
git blame filename
# To sync a fork with the master repo:
git remote add upstream git@github.com:name/repo.git # Set a new repo
git remote -v # Confirm new remote repo
git fetch upstream # Get branches
git branch -va # List local - remote branches
git checkout master # Checkout local master branch
git checkout -b new_branch # Create and checkout a new branch
git merge upstream/master # Merge remote into local repo
git show 83fb499 # Show what a commit did.
git show 83fb499:path/fo/file.ext # Shows the file as it appeared at 83fb499.
git diff branch_1 branch_2 # Check difference between branches
git log # Show all the commits
git status # Show the changes from last commit
# Commit history of a set of files
git log --pretty=email --patch-with-stat --reverse --full-index -- Admin\*.py > Sripts.patch
# Import commits from another repo
git --git-dir=../some_other_repo/.git format-patch -k -1 --stdout <commit SHA> | git am -3 -k
# View commits that will be pushed
git log @{u}..
# View changes that are new on a feature branch
git log -p feature --not master
git diff master...feature
# Interactive rebase for the last 7 commits
git rebase -i @~7
# Diff files WITHOUT considering them a part of git
# This can be used to diff files that are not in a git repo!
git diff --no-index path/to/file/A path/to/file/B
# To pull changes while overwriting any local commits
git fetch --all
git reset --hard origin/master
# Update all your submodules
git submodule update --init --recursive
# Perform a shallow clone to only get latest commits
# (helps save data when cloning large repos)
git clone --depth 1 <remote-url>
# To unshallow a clone
git pull --unshallow
# Create a bare branch (one that has no commits on it)
git checkout --orphan branch_name
# Checkout a new branch from a different starting point
git checkout -b master upstream/master
# Reset local branch to upstream branch and then checkout it
git checkout -B master upstream/master
# Remove all stale branches (ones that have been deleted on remote)
# So if you have a lot of useless branches, delete them on Github and then run this
git remote prune origin
# The following can be used to prune all remotes at once
git remote prune $(git remote | tr '\n' ' ')
# Revisions can also be identified with :/text
# So, this will show the first commit that has "cool" in their message body
git show :/cool
# Undo parts of last commit in a specific file
git checkout -p HEAD^ -- /path/to/file
# Revert a commit and keep the history of the reverted change as a separate revert commit
git revert <commit SHA>
# Pick a commit from a branch to current branch. This is different than merge as
# this just applies a single commit from a branch to current branch
git cherry-pick <commit SHA1>
# Undo last commit
# If you want to nuke commit C and never see it again
# (F)
# A-B-C
# ↑
# master
git reset --hard HEAD~1
# Undo last commit
# If you want to undo the commit but keep your changes
# (F)
# A-B-C
# ↑
# master
git reset HEAD~1
# list files changed in ${commit_id}
git diff-tree --no-commit-id --name-only -r ${commit_id}
# list files changed in ${commit_id}, porcelain way, meant to be user facing
git show --pretty="" --name-only bd61ad98
# See everything you have done, across branches, in a glance,
# then go to the place right before you broke everything
git reflog
git reset HEAD@{hash}
# To move your most recent commit from one branch and stage it on TARGET branch
git reset HEAD~ --soft
git stash
git checkout TARGET
git stash pop
git add .Jekyll
#install jekyll
gem install bundler jekyll
#create new jekyll project
jekyll new my-awesome-site
#launch jekyll server. find at http://localhost:4000
bundle exec jekyll serveObscure but Useful
-
abor wrk: benchmarking web servers -
apg: generates random passwords -
bc: calculator
-
cal: nice calendar
-
column: format text fields into aligned, fixed-width columns or tables -
comm: compare sorted files line by line -
cssh: visual concurrent shell -
cut,pasteandjoin: data manipulation
-
dd: moving data between files or devices -
dmesg: boot and system error messages -
dstat: useful system stats -
env: run a command (useful in scripts) -
expandandunexpand: convert between tabs and spaces -
expr: perform arithmetic or boolean operations or evaluate regular expressions -
factor: factor integers
-
file: identify type of a file -
fmt: format text paragraphs -
fold: wrap lines of text - glances: high level, multi-subsystem overview
- gpg: encrypt and sign files
-
hdparm: SATA/ATA disk manipulation/performance -
hostanddig: DNS lookups -
htop: improved version of top -
iconvoruconv: conversion for text encodings -
id: user/group identity info - iftop or nethogs: network utilization by socket or process
-
iostat: Disk usage stats -
last: login history -
ldd: dynamic library info -
lockfile: create semaphore file that can only be removed byrm -f -
logrotate: rotate, compress and mail logs. -
look: find English words (or lines in a file) beginning with a string -
lsblk: list block devices: a tree view of your disks and disk partitions -
lshw,lscpu,lspci,lsusb,dmidecode: hardware information, including CPU, BIOS, RAID, graphics, devices, etc. -
lsmodandmodinfo: List and show details of kernel modules. -
lsof: process file descriptor and socket info -
m4: simple macro processor - mtr: better traceroute for network debugging
-
mpstat: CPU usage stats -
nc: network debugging and data transfer - ngrep: grep for the network layer
-
nl: add line numbers -
nm: symbols from object files -
pr: format text into pages/columns -
printenv: print out environment variables (useful in debugging and scripts) -
rsync: sync files and folders over SSH or in local file system - sar: historic system stats
-
seq: print numbers - slurm: network traffic visualization
-
socat: socket relay and tcp port forwarder (similar tonetcat) -
splitandcsplit: splitting files -
sponge: read all input before writing it, useful for reading from then writing to the same file, e.g.,grep -v something some-file | sponge some-file -
ss: socket statistics -
stat: file info -
strace: system call debugging -
strings: extract text from binary files -
sysctl: view and configure Linux kernel parameters at run time -
tac: print files in reverse -
time: execute and time a command
-
timeout: execute a command for specified amount of time and stop the process when the specified amount of time completes. -
toe: table of terminfo entries -
tr: character translation or manipulation -
tree: display directories and subdirectories as a nesting tree; likelsbut recursive
-
units: unit conversions and calculations; converts furlongs per fortnight to twips per blink
-
vmstat: Memory usage stats -
w: who's logged on -
watch: run a command repeatedly, showing results and/or highlighting changes
-
when-changed: runs any command you specify whenever it sees file changed. See
inotifywaitandentras well. - wireshark and tshark: packet capture and network debugging
-
xz: high-ratio file compression -
yes: print a string a lot -
fortune,ddate, andsl: um, well, it depends on whether you consider steam locomotives and Zippy quotations "useful"
-
find . | xargs wc -l: count lines of code in an entire project
Pdftk
# PDF toolkit.
# More information: <https://www.pdflabs.com/tools/pdftk-the-pdf-toolkit>.
# Extract pages 1-3, 5 and 6-10 from a PDF file and save them as another one:
pdftk input.pdf cat 1-3 5 6-10 output output.pdf
# Merge (concatenate) a list of PDF files and save the result as another one:
pdftk file1.pdf file2.pdf … cat output output.pdf
# Split each page of a PDF file into a separate file, with a given filename output pattern:
pdftk input.pdf burst output out_%d.pdf
# Rotate all pages by 180 degrees clockwise:
pdftk input.pdf cat 1-endsouth output output.pdf
# Rotate third page by 90 degrees clockwise and leave others unchanged:
pdftk input.pdf cat 1-2 3east 4-end output output.pdfPostgres
-- show null values at "null" in query result
\pset null 'null'# Dump entire database into gzip
pg_dump -Ox database_name | gzip > vpdf.dump.gz
# Drop db and create new one from a gzip
dropdb old_db_name; createdb new_db_name; gzip -dc vpdf.dump.gz | psql new_db_name >/dev/null
# Dump inserts of just one table of a database
pg_dump -ROxa --inserts -t table_name database_name
#Show all processes running in postgres
ps -fu postgres-- Terminate all connections to a database inorder to drop it
-- Prevent all future connections
REVOKE CONNECT ON DATABASE thedb FROM public;
-- Terminate all connections except your own
SELECT pid, pg_terminate_backend(pid)
FROM pg_stat_activity
WHERE datname = current_database() AND pid <> pg_backend_pid();-- Rename a database that you are connected to
db=# \connect postgres;
-- terminate all the connections to the db database using the following statement:
postgres=# SELECT
pg_terminate_backend (pid)
FROM
pg_stat_activity
WHERE
datname = 'db';
-- rename the db database to newdb using the ALTER DATABASE RENAME TO statement as follows:
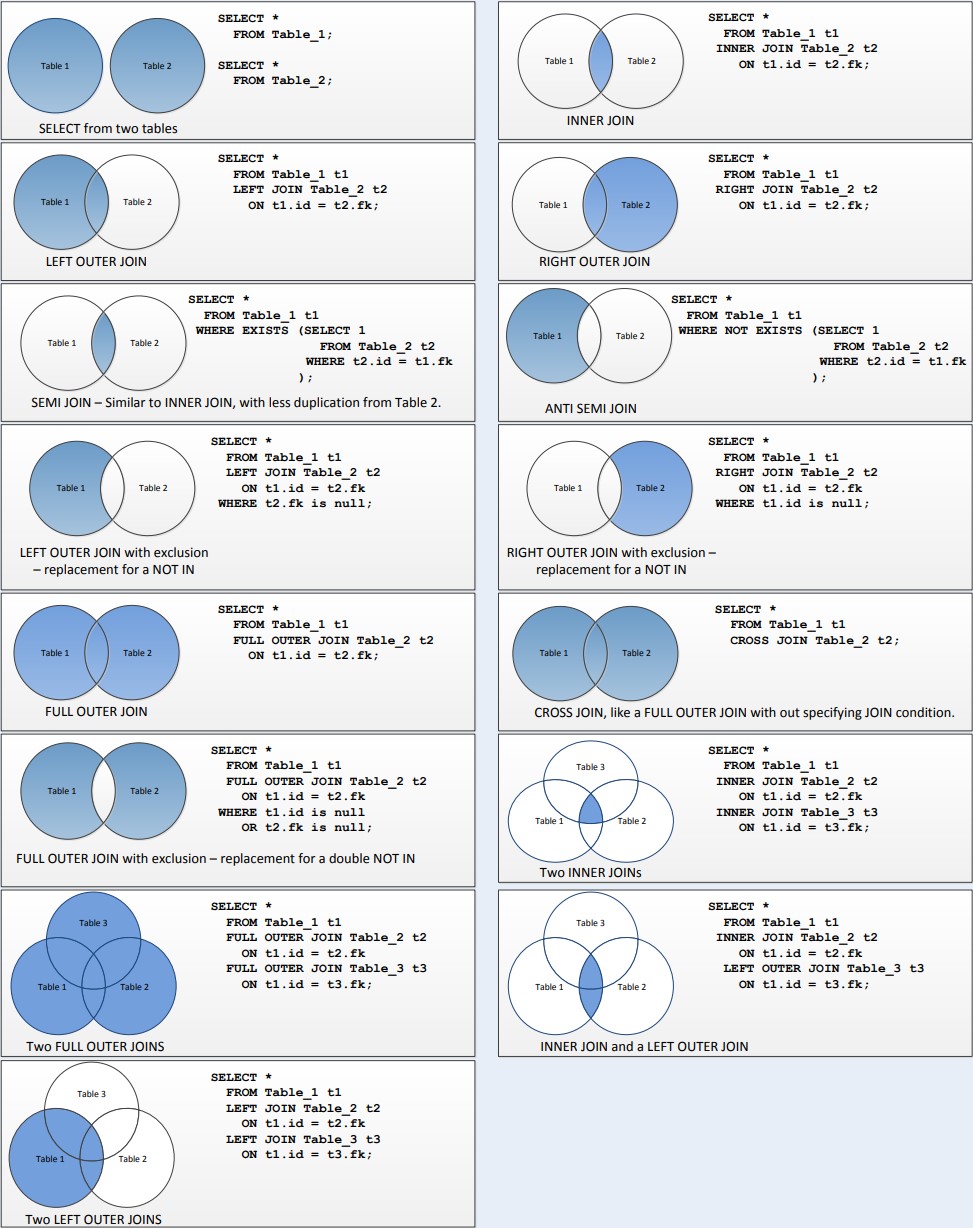
ALTER DATABASE db RENAME TO newdb;SQL Joins
Processes
# To list every process on the system:
ps aux
# To list a process tree
ps axjf
# To list every process owned by foouser:
ps -aufoouser
# To list every process with a user-defined format:
ps -eo pid,user,command
# Exclude grep from your grepped output of ps.
# Add [] to the first letter. Ex: sshd -> [s]shd
ps aux | grep '[h]ttpd'
#view process tree for a user
pstree <user>
#View all background process for a user
ps -ef | grep <user>Ruby on Rails
# Regnerate schema.rb file
bundle exec rake db:schema:dumpSSH Agent
#manually start ssh-agent
eval <code>ssh-agent</code>
#add ssh key
ssh-add- Auto start ssh-agent if it is not already running. (place in .bash_profile)
- This version is especially nice since it will see if you've already started ssh-agent and, if it can't find it, will start it up and store the settings so that they'll be usable the next time you start up a shell.
SSH_ENV="$HOME/.ssh/environment"
function start_agent {
echo "Initialising new SSH agent..."
/usr/bin/ssh-agent | sed 's/^echo/#echo/' > "${SSH_ENV}"
echo succeeded
chmod 600 "${SSH_ENV}"
. "${SSH_ENV}" > /dev/null
/usr/bin/ssh-add;
}
# Source SSH settings, if applicable
if [ -f "${SSH_ENV}" ]; then
. "${SSH_ENV}" > /dev/null
#ps ${SSH_AGENT_PID} doesn't work under cywgin
ps -ef | grep ${SSH_AGENT_PID} | grep ssh-agent$ > /dev/null || {
start_agent;
}
else
start_agent;
fiTail
# see last ten lines of a log file
tail some_file_name
# To show the last N lines of file
tail -n N file
# To show the last lines of file starting with the Nth
tail -n +N file
# To show the last N bytes of file
tail -c N file
# follow the last ten lines of a log file
tail -f some_file_nameVim
Shift + V
:sort 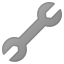 Developer Tools
Developer Tools
Cheatsheet Collections
| Dev Hints Cheatsheets |
|---|
| Bash Bible |
| The Art of Command Line |
| General Regex |
| Rest API |
| Vim |
| Markdown |
IDEs
Visual Studio Code
| Extensions | Version |
|---|---|
| Bash Beautifiy | 0.1.1 |
| Format in Context Menues | 1.0.4 |
| PostgreSQL.bout | 1.4.1 |
| Remote Development | 0.15.0 |
| Ruby | 0.22.3 |
VSCODE Remote Development Startup
F1 => Remote-SSH: Connect to Host... => user@hostname
Dash
Markdown
DB Modeling
Chrome Extensions
| Extensions | Version |
|---|---|
| Markdown Viewer | 3.6 |
| JSON Viewer | 0.18.0 |
| Stylish | 2.0.9 |
 Charts
Charts
Android Distribution Chart